In the realms of Fintech and digital UX consulting, service blueprints emerge as critical instruments for elucidating and refining the complex interplay between technological solutions and user experiences. They enable organizations to identify service gaps, streamline operations, and enhance the overall digital service performance, thereby elevating the customer experience to new levels. In other words: service blueprints are your roadmap to seamless customer journeys. Let’s learn main challenges of creating and utilizing a service blueprint in business.
What is a service blueprint?
A service blueprint stands as a strategic tool designed to visually document a service's operational processes, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of the service from both the provider's and the customer's perspectives. It encapsulates not only the customer's journey (customer journey map, CJM) but also the visible and invisible elements that contribute to the delivery of the service, such as the roles of front-end and back-end staff, digital interfaces, and the infrastructural support mechanisms.
Service blueprint at a glance
A service blueprint is a detailed visual map that outlines a service delivery process, capturing both customer interactions and the internal actions required to fulfill those interactions.
Key elements of a service blueprint
A service blueprint delineates several key components:
- Customer actions: The steps customers take as they interact with the service.
- Frontstage actions: Employee actions that occur in direct view of the customer, facilitating the service delivery.
- Backstage actions: Internal actions and decisions taken by employees that, while not visible to the customer, are essential for the service's provision.
- Support processes: The infrastructure and systems that underpin the service's delivery, ensuring that frontstage and backstage actions can be performed effectively.
- Physical evidence: Tangible artifacts that customers interact with throughout their journey, providing a physical dimension to the digital service.
What is a line of visibility?
In the context of a service blueprint, the "line of visibility" is a demarcation line that separates all the service actions visible to the customer (frontstage actions) from those that are invisible (backstage actions). It's a crucial concept that helps in designing and analyzing services by clearly illustrating which parts of the service process the customer can see and interact with, and which parts are internal operations meant to support the visible service functions. This distinction is essential for understanding and improving the customer experience, as it allows service designers to focus on optimizing both the visible service elements and the behind-the-scenes activities that support them.
What is line of interaction?
The "line of interaction" in a service blueprint refers to the boundary that delineates the direct interactions between the customer and the service provider. It highlights where and how customers engage with the service, encompassing all points of contact, from initial inquiry to service delivery and follow-up. This line is critical for understanding the customer journey, as it maps out every touchpoint where the customer actively participates in the service, allowing businesses to identify opportunities for enhancing service quality and customer satisfaction.
Practical applications of service blueprints in digital services
Service blueprinting facilitates a deep dive into the customer's experience, offering actionable insights that can lead to significant improvements in service design and delivery. For instance, by identifying bottlenecks or points of friction within the customer journey, businesses can prioritize developmental tasks and optimize interactions, thereby enhancing user satisfaction and loyalty.
- Deep dive into customer experience: Service blueprints allow businesses to thoroughly understand the customer journey, identifying both obstacles and areas of strength to inform strategic improvements in service design and delivery.
- Identification and optimization: By pinpointing critical touchpoints, companies can address bottlenecks, streamline processes, and enhance user interactions, leading to a more intuitive and satisfactory service.
- Enhances collaboration: They facilitate cross-departmental cooperation, offering a shared framework for understanding service delivery, thus fostering unified improvements across different areas of the business.
- Future-proofing services: Mapping the service journey helps anticipate customer needs and adapt to evolving expectations, keeping businesses ahead of market changes.
- Foundation for innovation: Beyond addressing current issues, service blueprints aid in the design of new services, ensuring every element is crafted with the customer's needs in mind, enhancing retention and satisfaction.
6 main customer pain points addressed by service blueprints
Service blueprints address several customer pain points, including:
- Confusing processes: They clarify complex service pathways, making interactions smoother.
- Long wait times: By optimizing workflows, blueprints can reduce delays.
- Inconsistent service quality: Standardizing service delivery improves reliability and satisfaction.
- Lack of personalization: Identifying touchpoints for customization enhances the individual experience.
- Difficulty in accessing support: Streamlining support channels ensures easier and quicker help.
- Navigational challenges in digital platforms: Simplifying user interfaces and improving UX design based on blueprint insights.
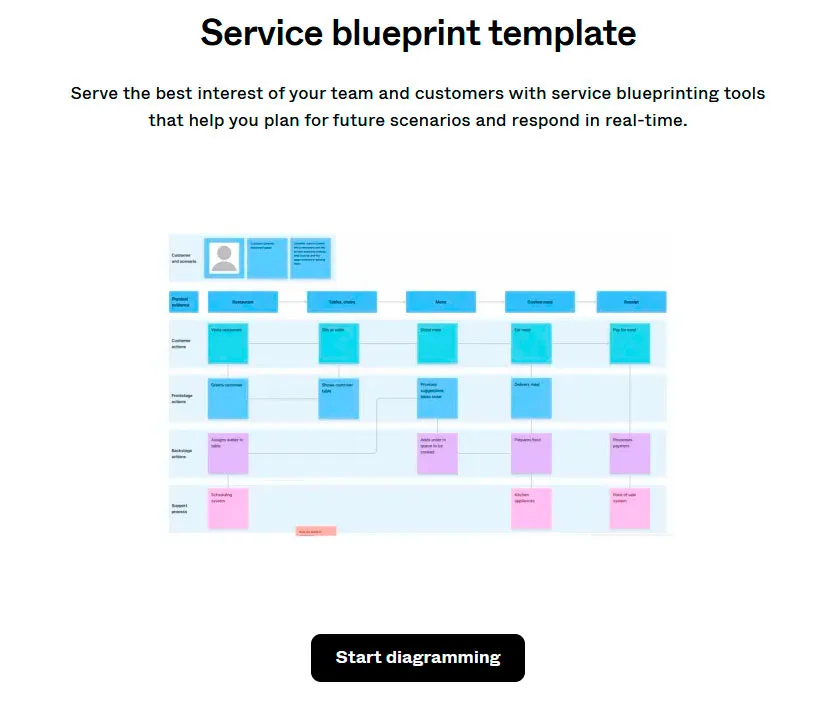
Service blueprint template in Figma
Service blueprint example
Service blueprint examples offer tangible insights into the practical application of this strategic tool, showcasing its versatility in enhancing various aspects of service delivery. Below, we explore real-world scenarios where service blueprints have been instrumental in identifying improvements and implementing effective solutions.
1. Online banking account opening
Situation: A bank seeks to optimize its online account opening process to improve customer satisfaction and reduce drop-off rates.
Service blueprint components:
- Customer actions: The customer navigates to the bank's website, selects the type of account they wish to open, fills in personal information, uploads necessary documents, and finally, submits the application.
- Frontstage actions: A customer service representative reviews the submitted application and documents. If any issues or questions arise, they contact the customer directly.
- Backstage actions: The system automatically checks the application against regulatory compliance requirements and performs a credit check.
- Support processes: Integration with third-party verification services to validate identity and documents without manual input.
- Physical evidence: Email confirmations of application receipt, progress updates, and account approval notification.
Outcome: The service blueprint identifies a bottleneck in document upload due to file size restrictions, leading to a high drop-off rate. By increasing the file size limit and offering alternative document submission methods, the bank streamlines the process, enhancing user satisfaction and reducing application abandonment.
2. E-commerce product return
Situation: An e-commerce platform wants to simplify its product return process to enhance customer loyalty and trust.
Service blueprint components:
- Customer actions: The customer logs into their account, selects the order from their purchase history, initiates a return request, and follows instructions for shipping the product back.
- Frontstage actions: Customer support approves the return request and provides the customer with a prepaid shipping label and return instructions via email.
- Backstage actions: Logistics partners notify the e-commerce platform upon receiving the returned product, triggering a quality check and refund process.
- Support processes: Automated systems update the order status throughout the return process, keeping the customer informed via email and in-app notifications.
- Physical evidence: Prepaid shipping label, return instructions email, refund transaction email.
Outcome: The blueprint uncovers that customers often find the return initiation process confusing, leading to increased calls to customer service. Simplifying the return initiation interface and providing clearer instructions reduces customer frustration and support calls, improving the overall return experience.
3. Restaurant reservation and dining experience
Situation: A high-end restaurant aims to refine its reservation and dining experience to ensure high customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Service blueprint components:
- Customer actions: The customer makes a reservation online, receives a confirmation, dines at the restaurant, and provides feedback through a follow-up email survey.
- Frontstage actions: The hostess confirms the reservation, greets the customer upon arrival, and escorts them to their table. Waitstaff serve the customers throughout their meal.
- Backstage actions: The kitchen staff prepare the meal according to the order. The management team reviews feedback from the follow-up surveys to identify areas for improvement.
- Support processes: The reservation system automatically sends a confirmation and reminder emails. A customer relationship management (CRM) system gathers and analyzes feedback data.
- Physical evidence: Reservation confirmation email, dining atmosphere, quality of food, follow-up feedback survey email.
Outcome: The service blueprint highlights that feedback is often not systematically used to improve the dining experience. Implementing a more structured process for analyzing feedback and making continuous improvements based on diners' suggestions enhances the quality of service and customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and word-of-mouth recommendations.
Markswebb's approach to service blueprinting
In the context of Markswebb's consultancy in Fintech and digital UX, service blueprints are leveraged to drive innovation and excellence in digital service delivery. Through a methodical approach that includes user research, benchmarking, and UX audits, Markswebb help to crafts blueprints that align digital services with business objectives, ensuring personalized, performance-oriented solutions that resonate with end-users. Reach out to Markswebb to enhance your digital offerings.
7 Tips for effectively creating a service blueprints and applying them
- Understand the elements: Begin by familiarizing yourself with the key elements of a service blueprint: customer actions, frontstage and backstage interactions, support processes, and the physical evidence that customers interact with. A clear understanding of these components is crucial for accurately mapping the service delivery process.
- Use examples and templates: Leverage existing service blueprint examples and templates as a starting point. Service Blueprint templates can be found on design and UX websites, professional design tool platforms (like Lucidchart, Miro, or Sketch), and through specialized service design and customer experience communities and forums. These resources can offer valuable insights and save time, making it easier to design a new service or improve an existing one.
- Focus on the design process: Incorporate design thinking into the blueprint creation to ensure that the service is user-centric. Focus the design process on solving real problems and addressing the needs of both the customers and the business.
- Visualize the Entire Service Journey: Service blueprints allow you to visualize the entire customer journey, highlighting all the touchpoints and interactions with your service. This comprehensive view is instrumental in identifying areas for improvement and innovation.
- Identify and Analyze Internal Interactions: Pay close attention to the line of internal interaction. Understanding the roles and responsibilities of those involved in the service process helps in pinpointing inefficiencies and areas where communication can be enhanced to deliver a smoother service experience.
- Apply the Blueprint for Innovation: Use the service blueprint as a tool not just for identifying problems but also for service innovation. It can guide you in designing new services or refining your service offering by revealing opportunities for enhancing service quality and customer satisfaction.
- Iterate and Improve: Service blueprints should not be static; they are part of an ongoing approach to service design and improvement. Regularly update your blueprint to reflect changes in your service delivery process or customer expectations. This iterative process ensures your service remains effective and competitive.
By integrating these tips, organizations can create effective service blueprints that not only illuminate the current state of service delivery but also pave the way for meaningful improvements and innovations.
Conclusion: benefits of service blueprinting
Understanding and implementing service blueprints is imperative for businesses aiming to navigate the complexities of digital service provision successfully. It offers a structured yet flexible framework for analyzing and improving every facet of the service experience. As digital landscapes evolve, the role of service blueprints in fostering innovative, user-centric solutions becomes increasingly significant, underscoring their value as an indispensable tool in the Fintech and digital UX consulting domains.

