Usability testing is a critical evaluation method used to assess how easily users can navigate and interact with a product or service. This process involves observing real users as they complete specific tasks, providing valuable insights into the user experience (UX) and identifying any issues that may hinder their interaction. The goal is to enhance the product’s usability, ensuring it meets the needs and expectations of its intended audience.
Contents
Usability testing holds significant importance across various industries. In digital banking and finance, it plays a pivotal role in ensuring that online platforms and applications are user-friendly and efficient. As these sectors increasingly rely on digital solutions, the need for seamless and intuitive user experiences becomes paramount.
Usability testing helps identify potential problems early in the development process, allowing for timely adjustments and improvements that enhance overall user satisfaction and engagement.
Definition of usability testingUsability testing is a methodological approach used to evaluate a product or service by testing it with representative users. The primary purpose of usability testing is to identify usability issues, collect qualitative and quantitative data, and determine the overall user satisfaction with the product. By observing users as they attempt to complete tasks, usability testing provides direct input on how real users interact with the system, allowing developers to understand user behavior and pinpoint areas that need improvement.
The insights gained from usability testing are crucial for refining the user experience (UX). This process helps ensure that products are intuitive, efficient, and satisfying to use. In digital banking and finance, where user trust and ease of use are paramount, usability testing is indispensable for creating reliable and user-friendly interfaces.
Usability testing can be conducted through various methods, each suited to different testing goals and contexts. The main types of usability testing include:
Each type of usability testing offers unique advantages and can be selected based on the specific needs and constraints of the project. By employing a combination of these methods, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and improve their products accordingly.
Setting objectives for usability testing
The first step in usability testing is to clearly define the objectives. These objectives guide the entire testing process and help determine what aspects of the product or service will be evaluated. Objectives may include identifying specific usability issues, understanding user behavior, assessing the effectiveness of new features, or comparing different versions of a product. Clearly defined objectives ensure that the testing process remains focused and that the resulting data is relevant and actionable.
Selecting the right participants
Choosing the right participants is crucial for obtaining meaningful insights. Participants should represent the target user group of the product or service. This means considering factors such as demographics, experience levels, and usage patterns. The selection process may involve screening questionnaires to ensure that participants match the desired user profile. Having a representative sample helps ensure that the findings are applicable to the broader user base.
Designing effective test scenarios
Effective test scenarios are designed to mimic real-world tasks that users would perform with the product. These scenarios should align with the objectives of the usability test and be relevant to the participants’ typical interactions with the product. Test scenarios should be clear, concise, and free of bias to ensure that participants understand what is being asked of them. The design of these scenarios is critical, as it directly impacts the quality of the data collected.
Collecting and analyzing data
During usability testing, data is collected through various methods, including direct observation, video recordings, screen captures, and user feedback. The collected data can be both qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative data includes observations and user comments, providing insights into user behavior and preferences. Quantitative data includes metrics such as task completion rates, time on task, and error rates, offering measurable indicators of usability.
Analyzing this data involves identifying patterns, usability issues, and areas for improvement. It requires a systematic approach to ensure that findings are accurate and actionable. The analysis should lead to specific recommendations for enhancing the user experience, which can then be implemented and tested in subsequent usability studies.
Markswebb, with its extensive experience in conducting usability testing, utilizes proprietary methodologies to deliver exceptional user experience insights. Below, we showcase our case study examples as a testament to our expertise and innovative approaches.
How we increased sales via the website
How we increased engagement of credit card holders
How we put acquiring into the pocket
How we built market-leading chatbot
How we stimulated corporate business growth
These case studies demonstrate the value of thorough usability testing in improving digital products and services. By focusing on user experience, Markswebb has consistently helped clients achieve significant business results.
If you're looking to enhance your digital offerings and achieve similar success, consider partnering with Markswebb. Our expertise in usability testing and user experience design can help you create market-leading services that drive customer satisfaction and business growth.
The cost of usability testing can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the scope of the project, the number of participants, and the methods used. For a basic usability test involving five to ten participants, costs can range from $5,000 to $10,000. This typically includes participant recruitment, test facilitation, and analysis of results. More extensive testing, involving larger participant groups or multiple rounds of iterative testing, can range from $15,000 to $30,000 or more. Additionally, incorporating advanced tools such as AI-driven analysis or remote usability testing platforms can further influence the overall cost. While usability testing represents a significant investment, it is crucial for ensuring a high-quality user experience, ultimately leading to greater user satisfaction and product success.
Iterative testing and continuous improvement
Usability testing is most effective when it is conducted iteratively throughout the development process. Iterative testing involves conducting multiple rounds of testing, with each round informing subsequent design improvements. This approach allows for continuous refinement based on real user feedback, ensuring that usability issues are identified and addressed early. By implementing changes incrementally and testing them repeatedly, organizations can enhance the user experience progressively, resulting in a more polished and user-friendly final product.
Importance of real user feedback
Genuine user feedback is invaluable for usability testing. Real users provide insights that cannot be replicated through theoretical analysis or internal reviews. Their interactions with the product reveal practical challenges and unexpected behaviors that developers may not anticipate. Incorporating real user feedback helps ensure that the product meets the actual needs and expectations of its target audience. This feedback should be gathered from a diverse group of users to capture a wide range of experiences and perspectives.
Balancing quantitative and qualitative data
A comprehensive usability testing strategy balances both quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data provides measurable insights, such as task completion rates, time on task, and error frequencies. These metrics are essential for identifying specific usability problems and tracking improvements over time. Qualitative data, on the other hand, offers a deeper understanding of user behaviors, preferences, and frustrations. It includes user comments, observations, and emotional responses, which provide context to the numerical data. By combining both types of data, organizations can gain a holistic view of the user experience and make well-informed design decisions.
Incorporating usability testing into the development process
For usability testing to be truly effective, it must be integrated into the development process from the outset. This means planning for usability testing in the initial project phases, allocating resources for regular testing sessions, and ensuring that findings are promptly incorporated into design iterations. Cross-functional collaboration is essential, with UX designers, developers, and stakeholders working together to prioritize usability. Embedding usability testing into the development workflow promotes a user-centered approach, ensuring that usability is a core consideration throughout the product lifecycle.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can leverage usability testing to create superior digital experiences. In industries like digital banking and finance, where user satisfaction and efficiency are critical, these practices help build trust and loyalty among users, ultimately leading to greater success and competitive advantage.
Usability testing checklists and templates are essential tools that streamline the usability testing process and ensure comprehensive evaluation. A usability testing checklist typically includes key steps such as defining objectives, selecting participants, designing test scenarios, conducting tests, and analyzing data. These checklists help ensure that all critical aspects of usability testing are covered and that the process is consistent and repeatable.
Templates, on the other hand, provide structured formats for various usability testing documents, such as test plans, participant recruitment scripts, consent forms, and data collection sheets. They help standardize the documentation process, making it easier to organize and analyze the results. Using templates can save time and reduce errors, allowing teams to focus more on deriving actionable insights from the testing.
Incorporating usability testing checklists and templates into the workflow enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of usability studies. They serve as valuable resources for both novice and experienced UX professionals, ensuring that best practices are followed and that the testing process is thorough and systematic. By leveraging these tools, organizations can better understand user behavior, identify usability issues, and improve the overall user experience of their digital products.
There are several reputable resources online where you can find and download usability testing checklists and templates:
These platforms provide valuable tools to help streamline and enhance your usability testing processes.
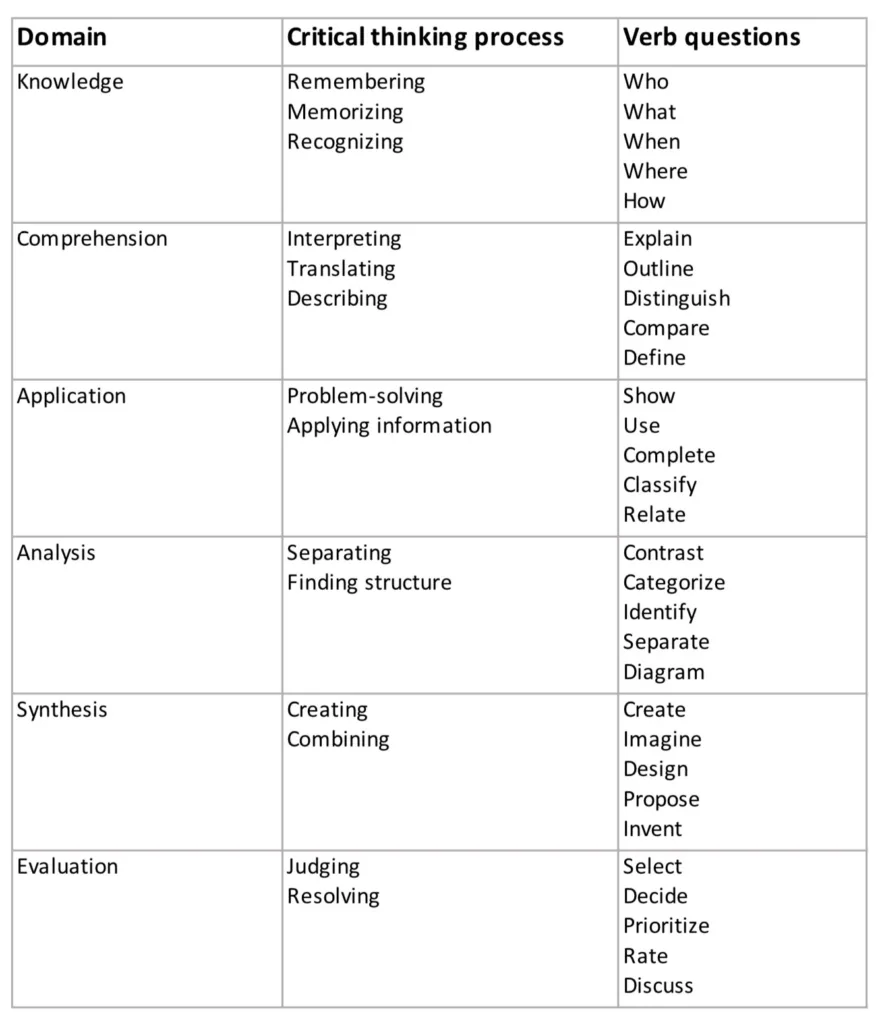
This is Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain chart from Nikki Anderson
Common challenges
Usability testing, while essential, is not without its challenges. One of the most common difficulties is recruiting participants who accurately represent the target user group. Finding and convincing suitable candidates to participate can be time-consuming and costly. Additionally, ensuring a diverse participant pool to get a comprehensive view of user behaviors and needs adds to the complexity.
Interpreting data from usability tests presents another significant challenge. Qualitative data, such as user comments and behaviors, can be subjective and difficult to quantify. On the other hand, quantitative data, while easier to measure, may not provide enough context to understand the underlying reasons for user actions. Balancing these data types to draw meaningful conclusions requires expertise and careful analysis.
Solutions and strategies to overcome these challenges
To address the challenge of recruiting participants, leveraging online platforms and professional networks can be effective. Utilizing social media, specialized user recruitment services, and engaging with user communities can help find suitable participants more efficiently. Offering incentives, such as monetary compensation or gift cards, can also increase participation rates.
For interpreting data, a mixed-methods approach that combines qualitative and quantitative analysis can be beneficial. Using tools and software designed for usability testing can help streamline data collection and analysis. Employing techniques such as thematic analysis for qualitative data and statistical analysis for quantitative data ensures a balanced and comprehensive understanding of the findings.
Clear objectives and well-defined metrics are crucial for effective data interpretation. Establishing specific goals for each test session and using consistent criteria to evaluate results helps maintain focus and objectivity. Regular training and collaboration among team members can enhance the accuracy and reliability of data interpretation.
By implementing these solutions and strategies, organizations can overcome common challenges in usability testing and leverage its full potential to enhance user experience. In sectors like digital banking and finance, where user interactions are critical, addressing these challenges ensures that usability testing provides actionable insights for continuous improvement.
Emerging trends
As technology continues to evolve, usability testing is also undergoing significant transformation. One of the most notable emerging trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into usability testing. AI-driven usability testing tools can automatically analyze user interactions, identify patterns, and predict potential usability issues. These tools enhance the efficiency and accuracy of usability testing by providing real-time insights and reducing the need for extensive manual analysis.
Another key trend is the increasing adoption of remote usability testing tools. These tools enable organizations to conduct usability tests with participants from diverse geographic locations, offering a broader perspective on user behavior. Remote usability testing is not only cost-effective but also allows for more flexible scheduling and a natural testing environment for participants. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of these tools, making remote testing a standard practice in many industries.
The growing importance of usability testing in an increasingly digital world
In today's digital-first world, the importance of usability testing cannot be overstated. As businesses across various sectors, particularly in digital banking and finance, continue to develop and deploy digital solutions, ensuring a seamless and intuitive user experience is paramount. Usability testing provides the insights needed to create products that meet user needs and expectations, fostering trust and satisfaction.
The shift towards digital services has also heightened user expectations. Users now demand more from their digital interactions, expecting intuitive, fast, and reliable experiences. Usability testing helps organizations stay ahead of these expectations by continuously refining their products based on real user feedback.
Moreover, the increasing complexity of digital products necessitates more sophisticated usability testing methods. With the advent of new technologies such as AI, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR), usability testing must adapt to evaluate these advanced interfaces effectively. This adaptation ensures that even the most cutting-edge products offer a user-friendly experience.
In conclusion, the future of usability testing is poised for innovation, driven by emerging technologies and the growing need for exceptional digital experiences. Organizations that prioritize usability testing and embrace these trends will be better positioned to meet the demands of an increasingly digital-savvy user base, securing a competitive edge in the market.
Our collection of articles, FAQs, and glossaries offers clear, concise explanations of widely used terms and concepts. Beyond definitions, the Handbook MW is a portal to understanding how these terms apply in real-world scenarios.
From research and analysis to strategy and design, we help our clients successfully reach their customers through digital services.
We respond to all messages as soon as possible.